A Listeria outbreak Tied to Deli-Sliced Meat has tragically claimed the lives of two individuals and led to the hospitalization of 28 others. This outbreak has impact on eleven states From Midwest and East Coast of the United States. The Most confirmed outbreaks occurred in Maryland and New York. Moreover two individuals passed away from this bacteria , it was held in New Jersey and Illinois.
Listeria is a dangerous bacterial infection spread through food, especially risky for pregnant people, seniors, kids, and those with weak immune systems. Symptoms like fever, muscle pain, and tiredness are common. Be cautious, especially after eating deli meats.
This Listeria outbreak has affected multiple states, leaving its impact as follows:
- Pennsylvania: Residents have been vigilant about food safety, particularly concerning deli meats.
- New Jersey: Health officials have issued warnings as Listeria infections have been reported.
- New York: This state has seen the highest number of infections, with seven cases reported.
- Maryland: Tragically, a fatality due to listeriosis occurred in this state.
- Other States: The outbreak has spread beyond these states to include Georgia, Illinois, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Missouri, North Carolina, Virginia, and Wisconsin.
Listeria Bacteria
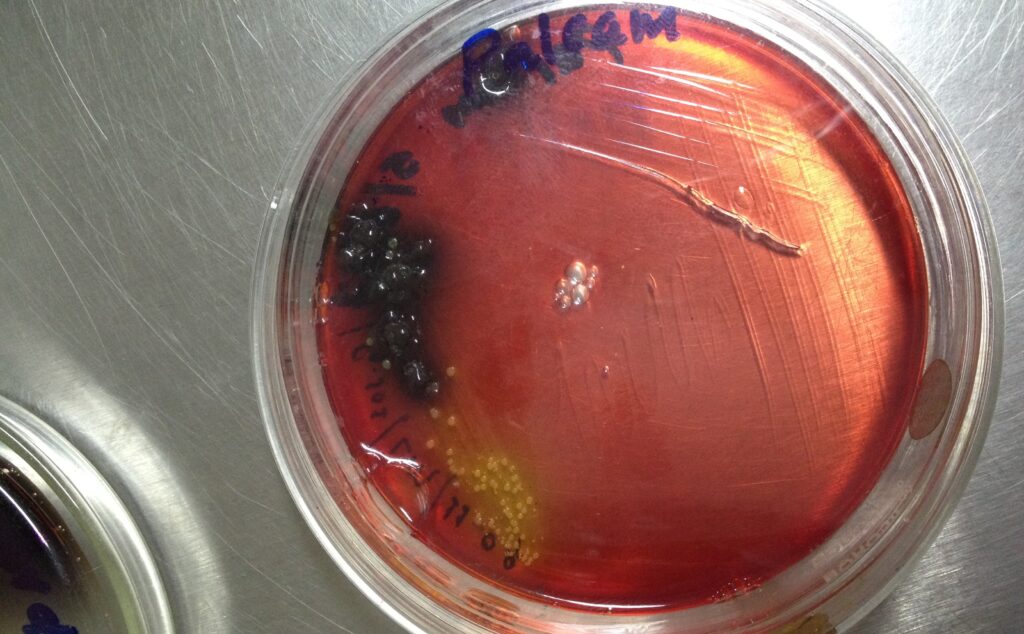
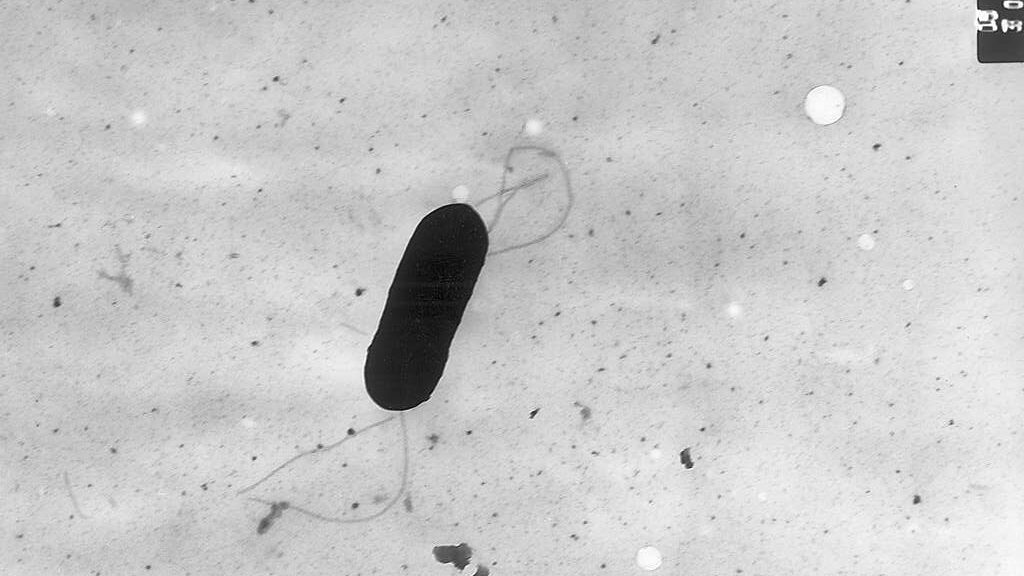
Listeria is a genus of bacteria known for its role as an intracellular parasite in mammals. Initially, 10 species of Listeria were recognized until 1992, each comprising two subspecies. As of 2024, the number of identified species has increased to 28. The genus honors Joseph Lister, a pioneer in sterile surgery.
Listeria species are Gram-positive, rod-shaped, facultatively anaerobic bacteria that do not form endospores. Among these, L. monocytogenes is the primary human pathogen, typically causing the rare bacterial infection known as listeriosis. This illness can result from consuming food contaminated with the bacterium and poses significant risks, particularly to pregnant women, newborns, immunocompromised individuals, and the elderly. In severe cases, it may lead to gastroenteritis.
Listeriosis is a serious human disease, with an acute form having a case-fatality rate of approximately 20–30%. The disease manifests primarily as sepsis and meningitis, with meningitis often complicated by encephalitis, a condition uncommon in bacterial infections. L-ivanovii, another species within the genus, primarily affects mammals, especially ruminants, and sporadically causes listeriosis in humans. The incubation period for listeriosis can range from three to 70 days.
Listeria Outbreak Background
Back in the late 1920s, two groups of researchers independently unmasked L. monocytogenes during animal outbreaks. They even gave it the name Bacterium monocytogenes. But alas, that name was already taken (by a slime mould and a protozoan, no less).
So, they put their thinking caps on, and voilà! The genus Listeria was born. It’s like the microbial version of “Choose Your Own Adventure.”
Listeria Causes:
Listeria bacteria can be found in various places:
- Soil and Water: Listeria can be present in soil, groundwater, and animal feces.
- Contaminated Food: Most cases of listeriosis result from consuming contaminated foods, including:
- Improperly Processed Deli Meats: Deli meats (such as ham, turkey, or salami) that have not been handled or cooked correctly.
- Unpasteurized Milk and Milk Products: Consumption of unpasteurized milk or products like soft cheeses.
- Certain Processed Foods: Soft cheeses, hot dogs, and deli meats that may become contaminated after processing.
Listeria Symptoms:
- If infected with Listeria, symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Muscle aches
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Symptoms typically appear within a few days after consuming contaminated food, but can manifest up to 30 days later.
- If the infection spreads to the nervous system, additional symptoms may include:
- Headache
- Stiff neck
- Confusion or changes in alertness
- Loss of balance
- Convulsions
Table of Contents
Risk Groups:
- Listeria infection is particularly severe for:
- Pregnant Women: Mild symptoms in mothers can lead to severe consequences for the baby.
- People Over 65: Weakened immune systems increase vulnerability.
- Unborn Babies: Transmission of Listeria from mother to baby during pregnancy is possible.
Prevention:
- To minimize the risk of listeria infection:
- Handle food with clean hands and in clean environments.
- Cook foods thoroughly and avoid consuming unpasteurized milk products.
- Exercise caution with deli meats and soft cheeses, ensuring they are properly stored and handled.
- Refrigerated pâté or meat spreads.
- Raw or lightly cooked sprouts.
- Choose These Instead
- Firm cheeses like cheddar and parmesan.
- Soft cheeses pasteurized and heated to at least 165°F or until steaming.Sliced deli cheeses heated to 165°F or until steaming.
- Store-bought deli salads (like coleslaw) over homemade.Sealed, airtight packages of refrigerated smoked fish.
- Thoroughly cook enoki mushrooms, especially if pregnant, over 65, or immunocompromised.
Related News
California Heat Wave: Record Break Temperatures In The Golden State.
